KU Initiative for Oxygen Crisis Management (KU-IOCM)
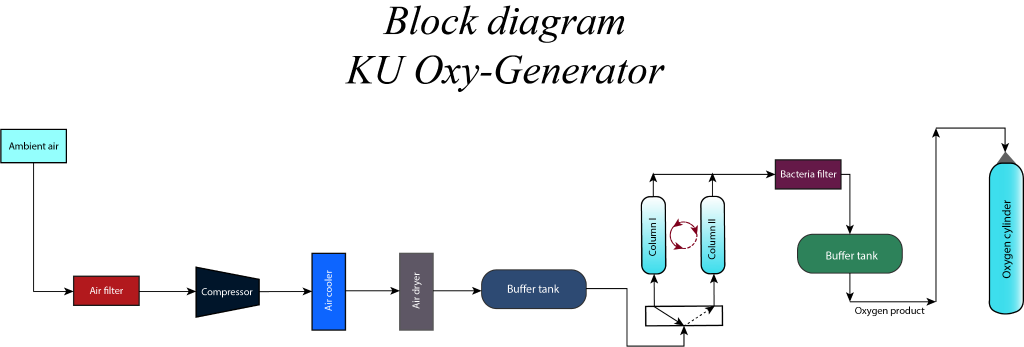
In this system, ambient feed air is drawn through a filter using a compressor operation at about 7 bar pressures. From the exit of the compressor, hot air comes out which is passed into a refrigerated air dryer to remove any moisture in the gas and also condenses any undesirable compounds. The buffer tank is also placed before the adsorption column to maintain the good flow of air into it. If by chance oil droplets are in the air, it is separated by using an oil separator before reaching into the adsorption column. The clean cool & dry air is finally sent through a pair of adsorber columns switching cyclically and undergoing a well-defined process to generate medical oxygen. The ideal temperature for the operation of adsorbers is 250 C. [1] The adsorption column works on the 5 steps. Then, the medical-grade oxygen is produced at the rate of 1.29 m^3 /hr.
Medical Oxygen Generation Principle
In this system, ambient feed air is drawn through a filter using a compressor operation at about 7 bar pressures. From the exit of the compressor, hot air comes out which is passed into a refrigerated air dryer to remove any moisture in the gas and also condenses any undesirable compounds. The buffer tank is also placed before the adsorption column to maintain the good flow of air into it. If by chance oil droplets are in the air, it is separated by using an oil separator before reaching into the adsorption column. The clean cool & dry air is finally sent through a pair of adsorber columns switching cyclically and undergoing a well-defined process to generate medical oxygen. The ideal temperature for the operation of adsorbers is 250 C. [1] The adsorption column works on the 5 steps. Then, the medical-grade oxygen is produced at the rate of 1.29 m^3 /hr.
Process Description
The oxygen generator works on the principle of swing adsorption. The system contains two adsorbers filled with Zeolite-13x as the main adsorbent for nitrogen. The generated oxygen is stored in a surge vessel and fulfills the requirements prescribed by Indian Pharmacopeia. The process involves following cyclic steps as described below in the figure.
Step 1. Feed Pressurization:
In this step, the feed air is passed through one of the adsorption columns/adsorbers to increase the pressure to the desired level. Throughout this step, the outlet valve is held closed, and only air is allowed to reach the adsorber column.
Step 2: Adsorption:
The adsorber column’s outlet valve is opened at the end of feed pressurization while the air inlet flow is maintained. During this process, air begins to enter the adsorber column while oxygen continues to leave the column, all while the column’s pressure remains constant. This is the primary step in which gas separation occurs and the desired purity of oxygen is made available at the outlet. During the separation of oxygen from the air, the bed material begins to accumulate Nitrogen, and for a certain amount of time, the bed material would be unable to retain any of the Nitrogen. The adsorption mechanism is halted just before this point by shutting the Oxygen discharge valve.
Step 3: Desorption:
The Nitrogen stored in the bed must be flushed out after the adsorption process is completed. This is accomplished by adding the column to the atmosphere while holding the air inlet and outlet closed. As the column is connected to the atmosphere, all of the adsorbed Nitrogen is flushed to the atmosphere, completing the desorption step.
Step 4: Purging:
Although much of the Nitrogen from the column is flushed during the desorption step, any residual Nitrogen remaining in the column voids and adsorbed to the surface of the bed material must be removed. This is accomplished by sending pure oxygen produced from the other column undergoing adsorption.
Step 5: Pressure Equalization:
To equalize pressure, both adsorbers are linked from the top to each other during this step. This is done to improve the system’s oxygen recovery
Progress
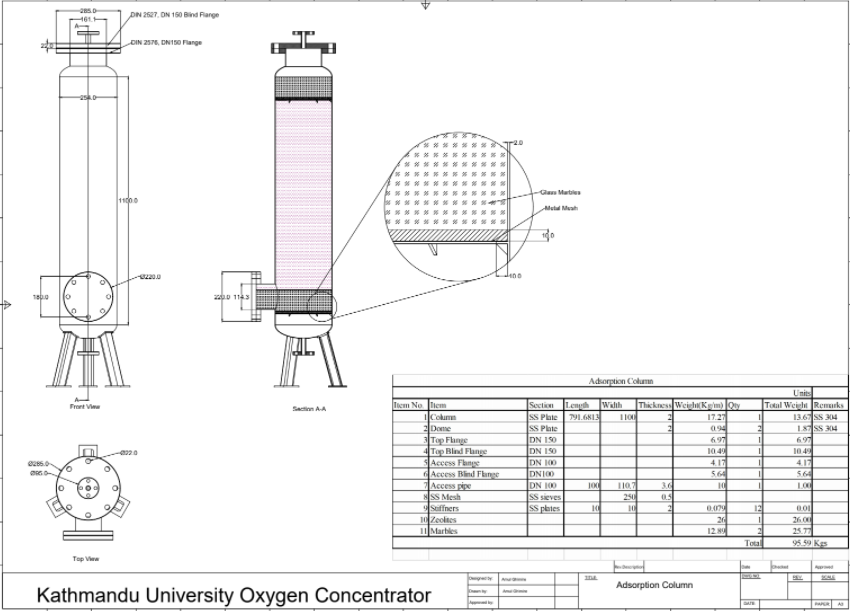
The KU-IOCM team has now completed the design and the calculations. The fabrication of the components required including adsorption columns and oxygen storage tank is completed. Procurement of equipment, assembly, and testing of the model is in progress
References
Shivapuji, Anand & S., Dasappa & Singh, Arashdeep. (2020). S3 – MEDICAL OXYGEN GENERATOR – An Indian Institute of Science Product. 10.13140/RG.2.2.11146.82887.
